
Keeping Motor At Correct Temperature When Connected To a Frequency Converter (photo by Yaconto LLC.)
Two types of influence
When a motor is connected to a frequency converter it must be kept at the correct temperature, and this is subject to two types of influence:
- If the speed decreases, the cooling air volume goes down.
- If a non-sinusoidal motor current is present, more heat is generated in the motor.
At low speeds the motor fan is not able to supply enough air for cooling. This problem arises if the load torque is constant throughout the control range.
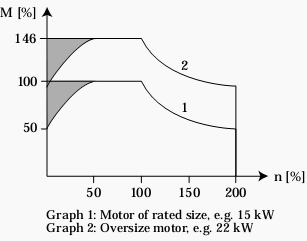
Figure 1 - The need for external ventilation for a motor at rated size and an oversize motor
If the motor runs continuously – at 100% rated torque – at a speed which is less than half the rated speed, the motor requires extra air for cooling (the grey areas in Figure 1).
Alternatively the load ratio of the motor can be reduced by selecting a bigger motor. However, care must be taken not to oversize the motor too much for a given frequency converter.
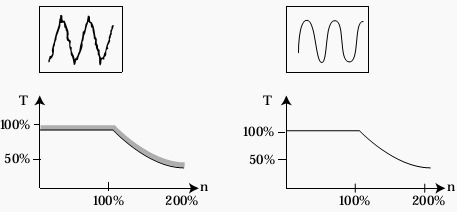
Figure 2 - A non-sinusoidal current generates extra heat in the motor
Reference: Fact Worth Knowing about Frequency Converters – Danfoss